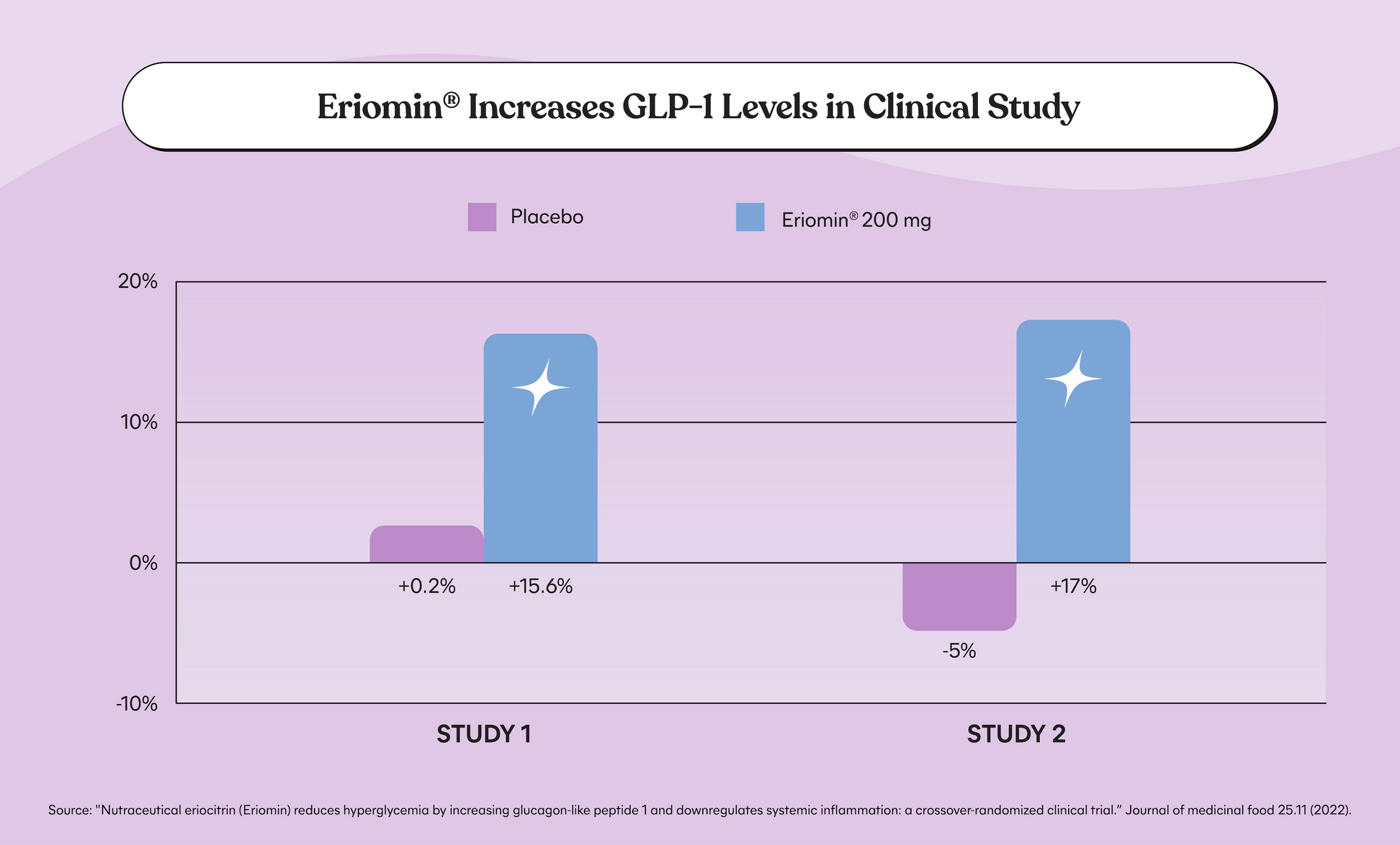
GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists have transformed the treatment landscape for diabetes and obesity, but understanding their potential side effects is essential for ensuring safe and effective management. These innovative medications mimic the natural hormone GLP-1, which plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. While offering significant health benefits, it’s vital to be aware of their side effects to make informed decisions about their use.
With the increasing prevalence of metabolic disorders, GLP-1-based therapies have become a cornerstone in modern healthcare. These treatments not only help stabilize blood glucose levels but also support weight loss, making them highly appealing to individuals with diabetes and obesity. However, as with any medication, they come with potential risks and side effects that warrant careful consideration.
This in-depth guide explores the side effects of GLP-1 medications, shedding light on their mechanisms, benefits, and risks. Whether you're a patient or a healthcare professional, gaining a comprehensive understanding of these aspects is key to optimizing treatment outcomes and ensuring patient safety.
Read also:Maroon 5 Leinger A Comprehensive Guide To The Bands Iconic Song
Table of Contents
- Overview of GLP-1 Medications
- How GLP-1 Medications Function
- Frequent Side Effects of GLP-1 Medications
- Gastrointestinal-Related Side Effects
- Potential Pancreatic Concerns
- Risks of Hypoglycemia
- Weight Loss and Associated Effects
- Long-Term Implications and Considerations
- Strategies for Managing Side Effects
- Final Thoughts and Recommendations
Overview of GLP-1 Medications
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of medications specifically designed to address metabolic conditions such as type 2 diabetes and obesity. These drugs work by enhancing the effects of GLP-1, a naturally occurring hormone that regulates blood sugar and appetite. By mimicking GLP-1, they improve insulin secretion, reduce glucose production in the liver, and decrease food intake, offering dual benefits for managing both diabetes and weight.
The growing popularity of GLP-1 medications stems from their ability to effectively control blood sugar levels while promoting weight loss. However, it’s important to acknowledge that these drugs can produce side effects, ranging from mild to severe. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for ensuring safe and effective treatment.
Some of the most widely prescribed GLP-1 medications include semaglutide, liraglutide, and dulaglutide. Although these drugs share similar mechanisms, their side effects may vary based on individual responses and dosing schedules.
How GLP-1 Medications Function
GLP-1 receptor agonists operate by binding to GLP-1 receptors throughout the body, initiating a series of physiological responses. These include:
- Stimulating insulin release from the pancreas, particularly after meals.
- Inhibiting glucagon secretion, thereby reducing glucose production in the liver.
- Slowing down gastric emptying, which enhances satiety and reduces appetite.
These mechanisms contribute to improved glycemic control and weight management. However, the same actions that make GLP-1 drugs effective can also lead to side effects, particularly those affecting gastrointestinal function.
Frequent Side Effects of GLP-1 Medications
Although GLP-1 receptor agonists are generally well-tolerated, they can cause a variety of side effects. These are often mild and temporary, especially when the medication is introduced gradually. The most commonly reported side effects include:
Read also:Remy Lacroix 2025 The Future Of Luxury Watches Redefined
- Gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Headaches.
It’s important to note that these side effects usually decrease over time as the body adjusts to the medication. However, in some cases, more serious side effects may arise, requiring prompt medical attention.
Gastrointestinal-Related Side Effects
Understanding Their Impact on Digestion
Gastrointestinal issues are among the most commonly reported side effects of GLP-1 medications. These drugs slow down gastric emptying, which can lead to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea in some patients. While these symptoms are typically mild, they can be uncomfortable and may affect adherence to treatment.
Research indicates that starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help mitigate gastrointestinal side effects. Additionally, taking the medication with food may alleviate nausea in certain individuals. By implementing these strategies, patients can improve their tolerance and enhance treatment effectiveness.
Potential Pancreatic Concerns
Exploring the Risks
One of the more significant concerns associated with GLP-1 medications is the potential risk of pancreatitis. Although rare, acute pancreatitis has been reported in some patients using these drugs. Symptoms of pancreatitis include severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
While ongoing research continues to investigate this link, current evidence suggests that the risk is relatively low. Nevertheless, patients with a history of pancreatitis should exercise caution and consult their healthcare provider before beginning GLP-1 therapy. Regular monitoring and open communication with healthcare professionals are essential for ensuring safety.
Risks of Hypoglycemia
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is another potential side effect of GLP-1 medications, particularly when used in conjunction with other diabetes treatments such as sulfonylureas. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include dizziness, sweating, confusion, and a rapid heartbeat.
To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia, healthcare providers often adjust dosages of concurrent medications or recommend lifestyle modifications. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial for early detection and effective management. By working closely with healthcare professionals, patients can reduce the likelihood of hypoglycemic episodes.
Weight Loss and Associated Effects
The Influence on Body Composition
One of the standout benefits of GLP-1 medications is their ability to promote weight loss. By slowing gastric emptying and reducing appetite, these drugs help patients achieve significant reductions in body weight. However, rapid weight loss can sometimes lead to side effects such as fatigue, muscle weakness, or nutritional deficiencies.
Patients using GLP-1 medications for weight management should prioritize a balanced diet and regular exercise to support overall health. Consulting a nutritionist or dietitian can also be beneficial in ensuring adequate nutrient intake. By adopting a holistic approach, patients can optimize their weight loss journey while maintaining optimal health.
Long-Term Implications and Considerations
Evaluating Safety Over Time
While GLP-1 receptor agonists have demonstrated promising results in short-term studies, their long-term effects are still being studied. Some concerns include the potential for thyroid tumors, although current evidence suggests this risk is minimal in humans.
Patients considering long-term use of GLP-1 medications should undergo regular check-ups and screenings to monitor their health. Open communication with healthcare providers is essential for addressing any emerging concerns or side effects. By staying informed and proactive, patients can ensure their long-term well-being.
Strategies for Managing Side Effects
Tips for Enhancing Tolerance
To maximize the benefits of GLP-1 medications while minimizing side effects, patients can adopt several strategies:
- Begin with a low dose and gradually increase it according to your healthcare provider's recommendations.
- Take the medication with food to reduce nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Stay hydrated to alleviate symptoms like constipation or diarrhea.
- Monitor blood glucose levels regularly to prevent hypoglycemia.
- Report any persistent or severe side effects to your doctor promptly.
By taking a proactive and informed approach to side effect management, patients can achieve better outcomes and enhance their overall quality of life.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
GLP-1 receptor agonists have ushered in a new era in the treatment of diabetes and obesity, offering groundbreaking solutions for metabolic health. However, understanding their potential side effects is essential for ensuring safe and effective treatment. From gastrointestinal discomfort to pancreatic concerns, recognizing these risks enables patients and healthcare providers to optimize treatment strategies.
We invite you to share your experiences or questions in the comments below. For further insights into metabolic health and treatment options, explore our other articles or consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Data Sources:
- American Diabetes Association
- Mayo Clinic
- U.S. National Library of Medicine