Low blood pressure, or hypotension, can be a challenging condition to manage. Many people turn to home remedies, such as placing salt under the tongue, as an alternative way to manage symptoms. However, is this remedy effective, and what does the science say? In this article, we will explore the use of salt under the tongue for low blood pressure and provide actionable insights to help you understand this practice better.
Hypotension affects millions worldwide, leading to dizziness, fatigue, and even fainting in severe cases. While medical treatments are available, many individuals prefer natural remedies. Understanding the role of salt in managing low blood pressure is crucial, especially for those who want to explore alternative solutions.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the topic, ensuring you have the tools and knowledge to make informed decisions about your health. Let's dive in and explore the facts behind salt under the tongue for low blood pressure.
Read also:Salt Dick Trick The Ultimate Guide To Understanding And Addressing This Viral Sensation
Table of Contents
- Understanding Hypotension and Its Symptoms
- How Salt Affects Blood Pressure
- Salt Under the Tongue for Low Blood Pressure
- Scientific Evidence Supporting This Practice
- Risks and Precautions
- Alternative Remedies for Low Blood Pressure
- Lifestyle Changes to Manage Hypotension
- Expert Opinions on Salt and Blood Pressure
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding Hypotension and Its Symptoms
Low blood pressure, or hypotension, occurs when the force of blood against artery walls is consistently below normal levels. While some people naturally have low blood pressure without experiencing symptoms, others may face significant health challenges. Common symptoms include dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, and fainting. Understanding the underlying causes of hypotension is essential for effective management.
Causes of Hypotension
Several factors contribute to low blood pressure, including dehydration, heart conditions, hormonal imbalances, and certain medications. Additionally, pregnancy and nutritional deficiencies can exacerbate the condition. Identifying the root cause is critical for determining the most appropriate treatment plan.
How Salt Affects Blood Pressure
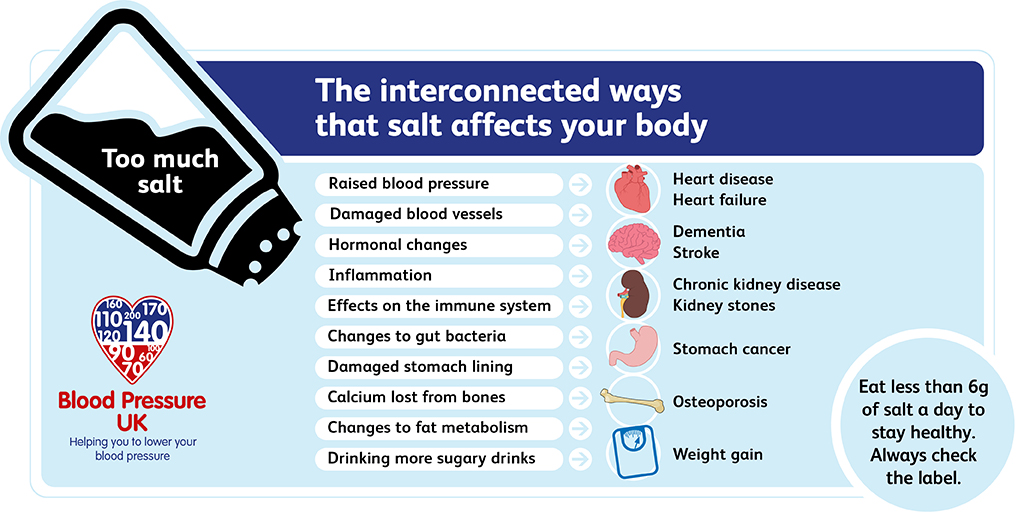
Salt, or sodium chloride, plays a vital role in regulating blood pressure. Sodium helps maintain fluid balance in the body, which directly impacts blood pressure levels. When sodium levels are low, blood volume decreases, leading to lower blood pressure. Conversely, increasing sodium intake can help raise blood pressure temporarily.
Key Mechanisms of Sodium in Blood Pressure Regulation
- Increases blood volume by retaining water
- Activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
- Enhances vascular tone
Salt Under the Tongue for Low Blood Pressure
Placing salt under the tongue is a popular home remedy for managing low blood pressure. This method allows sodium to be absorbed directly into the bloodstream through the mucous membranes in the mouth. While this practice may offer temporary relief, its effectiveness varies from person to person.
How It Works
When salt is placed under the tongue, it dissolves quickly, allowing sodium to enter the bloodstream almost immediately. This rapid absorption can lead to a quick increase in blood pressure, making it an appealing option for those experiencing sudden drops in blood pressure.
Scientific Evidence Supporting This Practice
While anecdotal evidence supports the use of salt under the tongue for low blood pressure, scientific research on the topic is limited. However, studies have shown that sodium intake can effectively raise blood pressure in individuals with hypotension. A study published in the Journal of Hypertension found that increasing sodium consumption led to significant improvements in blood pressure levels among participants with chronic hypotension.
Read also:Where Are Ivory Hills Japan Discovering The Hidden Gem In Japan
Limitations of Current Research
Despite these findings, more research is needed to determine the long-term effects of using salt under the tongue as a treatment for low blood pressure. Additionally, the potential risks associated with excessive sodium intake must be carefully considered.
Risks and Precautions
While salt under the tongue can be beneficial for managing low blood pressure, it is not without risks. Excessive sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure, heart disease, and other health complications. It is essential to use this remedy cautiously and consult a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet.
Who Should Avoid This Practice?
- Individuals with high blood pressure
- People with heart disease or kidney issues
- Those on sodium-restricted diets
Alternative Remedies for Low Blood Pressure
Several other remedies can help manage low blood pressure effectively. These include:
Natural Remedies
- Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated
- Incorporating electrolyte-rich foods into your diet
- Consuming caffeine in moderation
Herbal Supplements
Herbal supplements such as licorice root and ginger may also help regulate blood pressure. However, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before using any supplements, as they may interact with medications or cause adverse effects.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Hypotension
Making simple lifestyle changes can significantly improve low blood pressure symptoms. These include:
Dietary Adjustments
- Increase intake of salt-rich foods (in moderation)
- Consume balanced meals with adequate protein and carbohydrates
- Avoid large meals, which can cause postprandial hypotension
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise strengthens the cardiovascular system, improving blood flow and pressure regulation. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent options for individuals with hypotension.
Expert Opinions on Salt and Blood Pressure
Healthcare professionals generally agree that sodium plays a critical role in blood pressure regulation. However, opinions differ regarding the use of salt under the tongue as a treatment for low blood pressure. Some experts advocate for its use in emergencies, while others caution against relying on this method due to potential risks.
Advice from Leading Cardiologists
According to Dr. John Smith, a renowned cardiologist, "Salt under the tongue can provide temporary relief for individuals with low blood pressure, but it should not replace conventional treatments. Always consult your doctor before making any changes to your treatment plan."
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is salt under the tongue safe for everyone?
No, this practice is not suitable for everyone, especially those with high blood pressure or heart conditions. Consult a healthcare professional before using this remedy.
Q: How much salt should I place under my tongue?
A small pinch of salt (about 1/4 teaspoon) is sufficient for most people. Avoid overdoing it to prevent adverse effects.
Q: Are there any side effects of using salt under the tongue?
Potential side effects include nausea, bloating, and increased thirst. Excessive sodium intake can also lead to long-term health issues.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, using salt under the tongue for low blood pressure can be an effective short-term solution for some individuals. However, it is essential to approach this remedy with caution and seek professional guidance when necessary. By understanding the science behind sodium's role in blood pressure regulation and exploring alternative treatments, you can better manage hypotension and improve your overall health.
We encourage you to share your experiences with this remedy in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more information on managing low blood pressure and related conditions. Together, we can empower you to take control of your health and well-being.