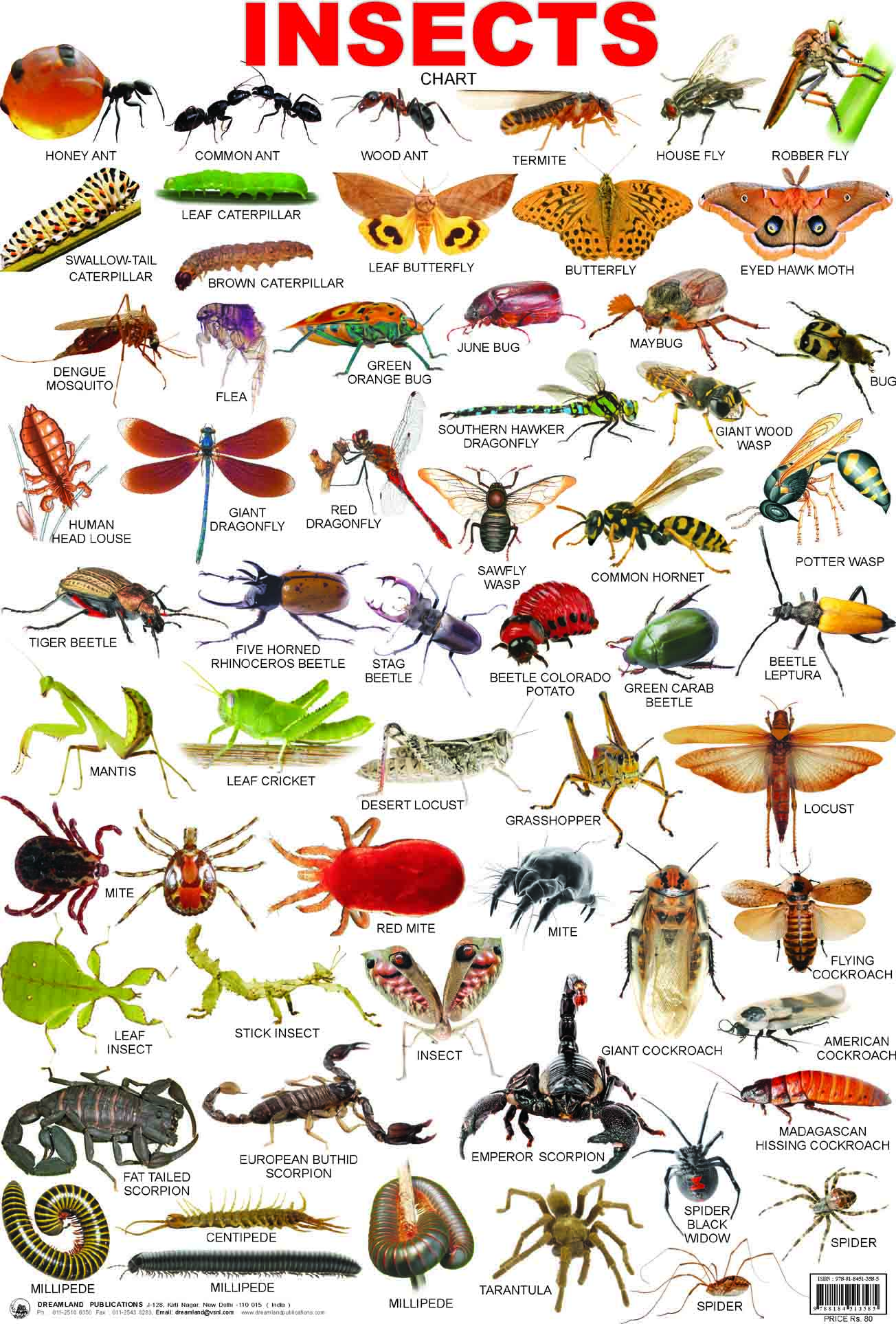
When we think about insects, we often focus on their present-day roles in ecosystems. However, understanding the first insects provides a window into the history of life on Earth. These ancient creatures were pioneers in the animal kingdom, shaping the environment and paving the way for modern biodiversity. In this article, we will delve into the origins and evolution of the first insects, uncovering their significance in the natural world.
The study of the first insects is a captivating journey through time. These tiny organisms played a crucial role in the development of terrestrial ecosystems, interacting with plants and other animals in ways that continue to influence life today. By exploring their early history, we gain insights into the complex interplay of evolution and adaptation.
As we explore the origins of the first insects, we will examine the scientific evidence that supports our understanding of their emergence. Through fossil records and genetic studies, researchers have pieced together the story of how these creatures evolved and diversified over millions of years. This article will provide a comprehensive look at this fascinating subject, ensuring that readers gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of insects in the history of life.
Read also:Will Smith Car Accident A Comprehensive Analysis Of The Incident And Its Impact
Table of Contents
- Origins of the First Insects
- Fossil Evidence of Ancient Insects
- Evolutionary Adaptations of the First Insects
- Biological Diversity in Early Insects
- Environmental Impact of the First Insects
- Key Species Among the First Insects
- Scientific Research on the First Insects
- Connections Between Ancient and Modern Insects
- The Importance of Studying the First Insects
- Future Studies on the First Insects
Origins of the First Insects
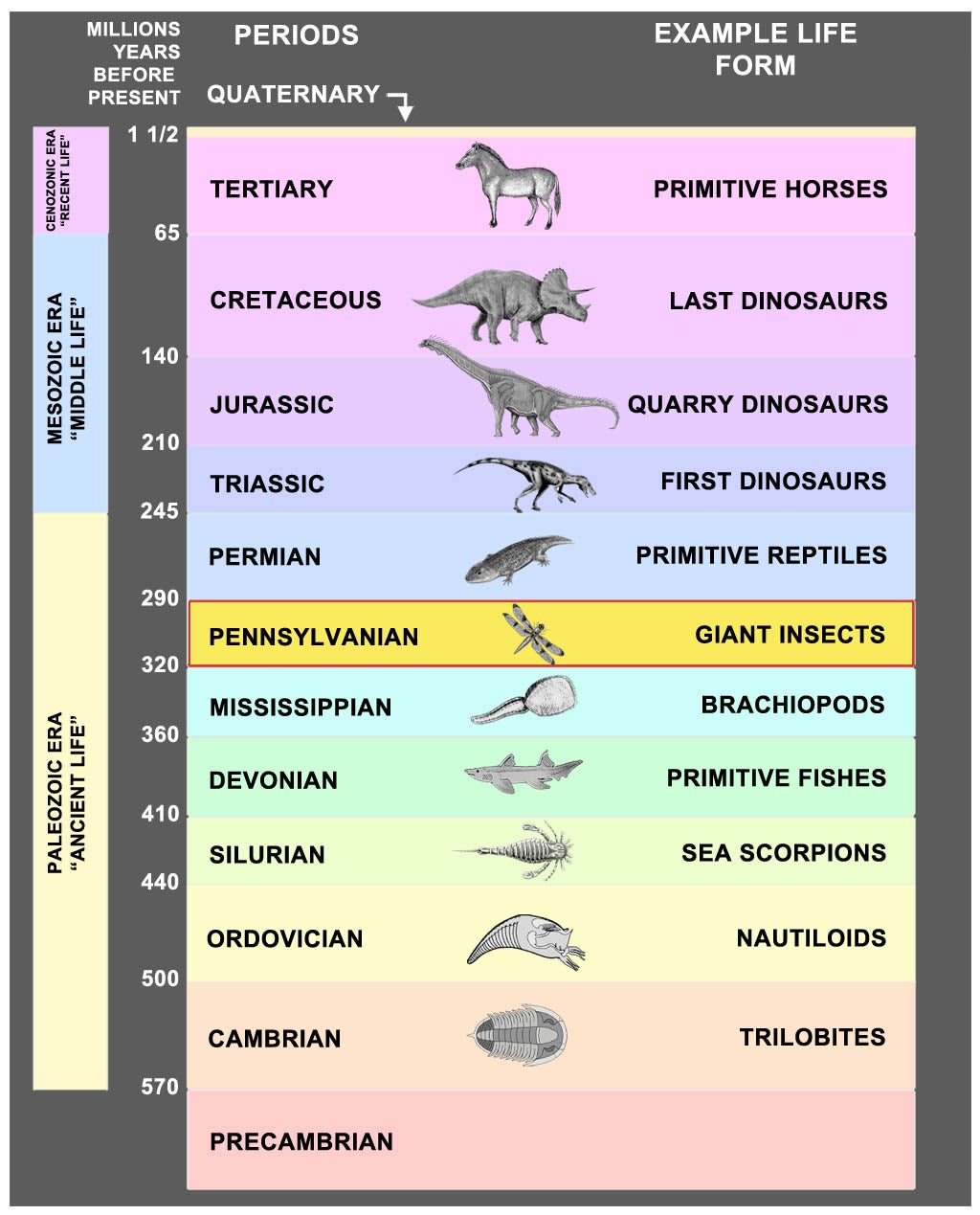
Understanding the origins of the first insects requires a deep dive into the geological timeline of Earth. These creatures appeared during the Devonian period, approximately 400 million years ago. This era marked a significant transition in the history of life, as terrestrial environments began to support complex ecosystems. The first insects likely evolved from primitive arthropods that inhabited aquatic environments, gradually adapting to life on land.
Transition from Aquatic to Terrestrial Life
The move from water to land was a monumental evolutionary leap for the ancestors of the first insects. These early arthropods developed several key adaptations that allowed them to survive in terrestrial habitats. For example, they evolved waterproof exoskeletons to prevent desiccation and specialized respiratory systems to extract oxygen from the air. These adaptations were crucial for their survival and eventual diversification.
Studies suggest that the first insects likely began as detritivores, feeding on decaying organic matter. Over time, they diversified into various ecological niches, including herbivory, predation, and parasitism. This diversification laid the foundation for the incredible variety of insects we see today.
Fossil Evidence of Ancient Insects
Fossils provide invaluable insights into the lives of the first insects. Although insects have soft bodies that do not fossilize well, scientists have discovered numerous specimens preserved in amber and sedimentary rocks. These fossils reveal details about the morphology, behavior, and ecological roles of ancient insects.
Significant Fossil Discoveries
- Rhyniognatha hirsti: One of the oldest known insect fossils, dating back to the Devonian period. This specimen provides evidence of early winged insects.
- Archaeognatha: Fossils of this group offer clues about the evolution of insect mouthparts and feeding strategies.
- Palaeodictyoptera: Large, winged insects from the Carboniferous period, these fossils demonstrate the diversity of early insect forms.
By analyzing these fossils, researchers can reconstruct the evolutionary pathways of the first insects and their descendants. Each discovery adds a piece to the puzzle of insect evolution, helping us understand how these creatures adapted to changing environments over millions of years.
Evolutionary Adaptations of the First Insects
The first insects exhibited a range of adaptations that enabled them to thrive in terrestrial ecosystems. These adaptations included the development of wings, specialized sensory organs, and reproductive strategies that increased their chances of survival.
Read also:Does The Salt Trick For Men Really Work Unveiling The Truth Behind This Popular Trend
Wings: A Key Evolutionary Innovation
The evolution of wings was one of the most significant developments in the history of insects. Wings allowed these creatures to explore new habitats, escape predators, and find mates more efficiently. Early winged insects, such as those in the order Palaeodictyoptera, had fixed wings that could not fold. Over time, insects evolved the ability to fold their wings, a feature that enhanced their mobility and versatility.
Other adaptations, such as compound eyes and antennae, improved the sensory capabilities of the first insects. These structures allowed them to detect light, movement, and chemical signals, giving them a competitive edge in their environments.
Biological Diversity in Early Insects
The first insects exhibited a remarkable degree of biological diversity, even in their early stages of evolution. This diversity was driven by the variety of ecological niches available in terrestrial ecosystems. Some insects evolved as herbivores, feeding on plants, while others became predators, preying on smaller arthropods.
Examples of Early Insect Diversity
- Herbivorous Insects: These insects adapted to feed on the leaves, stems, and roots of early land plants.
- Predatory Insects: Early predators developed specialized mouthparts for capturing and consuming prey.
- Parasitic Insects: Some insects evolved parasitic lifestyles, living on or inside other organisms.
This diversity laid the groundwork for the complex interactions between insects and other organisms that characterize modern ecosystems. By filling different ecological roles, the first insects contributed to the stability and resilience of terrestrial environments.
Environmental Impact of the First Insects
The emergence of the first insects had a profound impact on the environment. These creatures played important roles in nutrient cycling, pollination, and decomposition. Their activities helped shape the terrestrial ecosystems of their time and influenced the evolution of other organisms.
Key Roles of the First Insects
- Pollinators: Some early insects likely contributed to the pollination of plants, facilitating the reproduction of flowering plants.
- Decomposers: Insects that fed on decaying organic matter helped recycle nutrients back into the soil.
- Predators: By controlling populations of other arthropods, predatory insects maintained balance in their ecosystems.
These roles demonstrate the importance of the first insects in maintaining the health and productivity of terrestrial ecosystems. Their contributions to ecological processes continue to be felt today, as modern insects perform similar functions in our environment.
Key Species Among the First Insects
Several key species stand out in the study of the first insects. These species provide important insights into the early stages of insect evolution and the development of key adaptations.
Notable Species
- Rhyniognatha hirsti: One of the earliest known winged insects, this species offers evidence of the evolution of flight.
- Palaeodictyoptera: Large, winged insects from the Carboniferous period, these species demonstrate the diversity of early insect forms.
- Archaeognatha: Fossils of this group reveal the evolution of insect mouthparts and feeding strategies.
By studying these species, researchers can better understand the evolutionary pathways that led to the incredible diversity of modern insects.
Scientific Research on the First Insects
Scientific research on the first insects relies on a combination of fossil analysis, genetic studies, and ecological modeling. These approaches provide a comprehensive view of insect evolution and the factors that influenced their development.
Methods of Study
- Fossil Analysis: Examining fossilized remains to reconstruct the morphology and behavior of ancient insects.
- Genetic Studies: Using DNA analysis to trace the evolutionary relationships between modern and ancient insects.
- Ecological Modeling: Simulating the interactions between early insects and their environments to understand their ecological roles.
These methods have yielded valuable insights into the history of the first insects, helping scientists piece together the story of their origins and evolution.
Connections Between Ancient and Modern Insects
The legacy of the first insects is evident in the characteristics and behaviors of modern insects. Many of the adaptations that evolved in ancient insects persist in their descendants today, shaping the interactions between insects and their environments.
Shared Traits and Behaviors
- Wings: The ability to fly remains a defining feature of many modern insects.
- Specialized Mouthparts: Modern insects exhibit a wide variety of mouthparts adapted to different feeding strategies.
- Sensory Organs: Compound eyes and antennae continue to play crucial roles in insect perception and communication.
By studying the connections between ancient and modern insects, we gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary processes that have shaped life on Earth.
The Importance of Studying the First Insects
Studying the first insects is essential for understanding the history of life on Earth. These creatures played a vital role in the development of terrestrial ecosystems and influenced the evolution of other organisms. By examining their origins and evolution, we gain insights into the complex interplay of environmental factors and biological adaptations that drive evolutionary change.
Moreover, the study of the first insects has practical applications in fields such as agriculture, medicine, and conservation. Understanding the evolutionary history of insects can inform strategies for managing pests, developing new drugs, and preserving biodiversity.
Future Studies on the First Insects
Future research on the first insects promises to uncover new insights into their origins and evolution. Advances in technology, such as improved imaging techniques and genomic analysis, will enhance our ability to study these ancient creatures. Additionally, ongoing fossil discoveries will provide fresh data for scientists to analyze.
By continuing to explore the world of the first insects, we deepen our understanding of the natural world and our place within it. This research not only enriches our knowledge of the past but also informs our efforts to address the challenges of the present and future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the first insects were pivotal players in the history of life on Earth. Their emergence and evolution shaped terrestrial ecosystems and laid the foundation for the incredible diversity of modern insects. By studying these ancient creatures, we gain valuable insights into the processes of evolution and adaptation that continue to influence life today.
We invite you to explore further by leaving your thoughts in the comments section below or sharing this article with others who may find it interesting. For more fascinating articles on the natural world, be sure to check out our other content on the website. Together, let's continue to uncover the wonders of life on Earth!