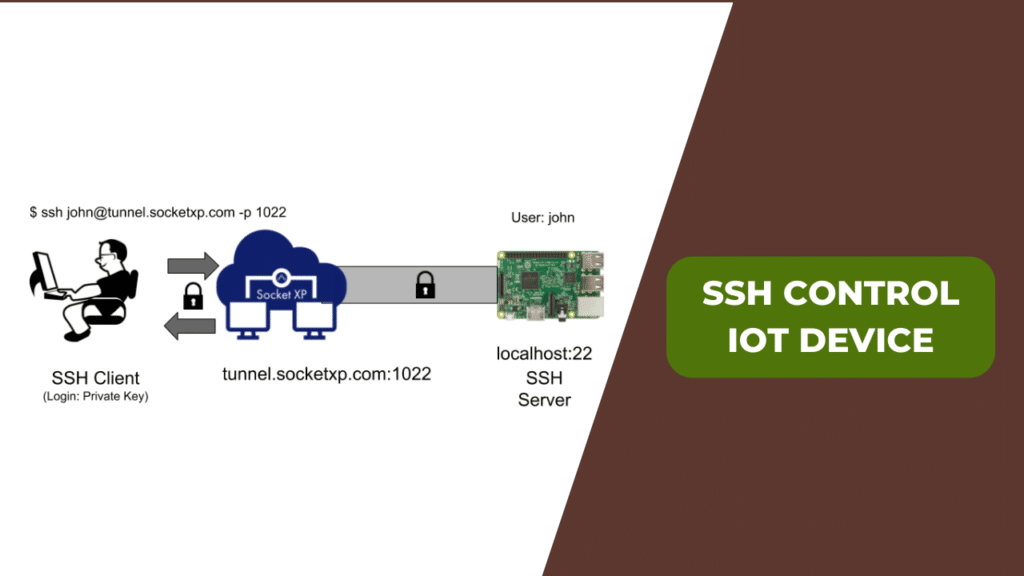
In today's interconnected world, IoT (Internet of Things) devices have become integral to our daily lives. Whether it's smart homes, industrial automation, or remote monitoring, these devices play a crucial role. However, managing and securing these devices remotely can be challenging, especially when it comes to accessing them via SSH (Secure Shell). This article provides an in-depth tutorial on accessing IoT devices using SSH, offering practical tips and expert advice to ensure seamless connectivity.
As the adoption of IoT continues to grow, understanding how to access and manage these devices is essential for both professionals and enthusiasts alike. By mastering SSH, you can securely interact with your IoT devices from anywhere in the world, ensuring efficient management and control.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about accessing IoT devices via SSH. From setting up your environment to troubleshooting common issues, we've got you covered. Let's dive in!
Read also:Does Putting Salt Under Your Tongue Do Anything Unveiling The Truth
Table of Contents
- Introduction to IoT Device SSH Access
- What is SSH?
- Overview of IoT Devices
- Setting Up SSH on IoT Devices
- Connecting Remotely via SSH
- Security Best Practices for SSH
- Troubleshooting Common SSH Issues
- Advanced Features and Configurations
- Real-World Use Cases of IoT SSH Access
- Future Trends in IoT and SSH
Introduction to IoT Device SSH Access
Accessing IoT devices via SSH has become a fundamental skill for anyone working in the field of IoT. SSH provides a secure way to connect to remote devices, allowing users to execute commands, transfer files, and manage configurations without physical access.
One of the key benefits of SSH is its encryption capabilities, ensuring that all data transmitted between your computer and the IoT device remains secure. This is particularly important when dealing with sensitive information or critical infrastructure.
What is SSH?
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol used to securely access remote devices. It provides a secure channel over an unsecured network, protecting against eavesdropping, data tampering, and other malicious activities.
Key Features of SSH
- Encryption: All data transmitted via SSH is encrypted, ensuring privacy and security.
- Authentication: SSH supports various authentication methods, including passwords, public key authentication, and multi-factor authentication.
- Portability: SSH can be used across different platforms and operating systems, making it versatile for various applications.
According to a report by Cisco, the number of IoT devices is expected to reach 75 billion by 2025. With such rapid growth, the importance of secure remote access cannot be overstated.
Overview of IoT Devices
IoT devices encompass a wide range of technologies, from simple sensors to complex industrial machinery. These devices are designed to collect, process, and transmit data, often in real-time, enabling smarter decision-making and automation.
Types of IoT Devices
- Consumer Devices: Smart thermostats, security cameras, and wearable devices.
- Industrial Devices: Sensors for monitoring equipment, smart grids, and robotics.
- Enterprise Devices: Networked printers, smart office solutions, and inventory management systems.
A study by Statista revealed that the global IoT market is projected to reach $1.5 trillion by 2025, highlighting the significant impact of these devices on various industries.
Read also:Lucy Wells Rising Star At Jersey Express
Setting Up SSH on IoT Devices
Before you can access your IoT device via SSH, you need to ensure that SSH is properly configured. This involves enabling the SSH service, setting up user accounts, and configuring firewall rules.
Steps to Enable SSH
- Log in to your IoT device using its local interface or web-based management console.
- Navigate to the settings or configuration menu and enable the SSH service.
- Set up user accounts with appropriate permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can access the device.
- Configure firewall rules to allow SSH traffic on port 22 (or a custom port if necessary).
It's important to note that not all IoT devices come with SSH pre-installed. In such cases, you may need to install an SSH server manually or use alternative methods for remote access.
Connecting Remotely via SSH
Once SSH is set up on your IoT device, you can connect to it remotely using an SSH client. There are several popular SSH clients available, including PuTTY for Windows, OpenSSH for Linux and macOS, and mobile apps for Android and iOS.
Connecting with OpenSSH
To connect to your IoT device using OpenSSH, open a terminal window and enter the following command:
ssh username@device_ip
Replace "username" with your actual username and "device_ip" with the IP address of your IoT device. If you're using a custom port, you can specify it using the "-p" option:
ssh -p custom_port username@device_ip
For added security, consider using public key authentication instead of passwords. This involves generating a key pair and adding the public key to the authorized_keys file on your IoT device.
Security Best Practices for SSH
While SSH is inherently secure, there are several best practices you can follow to further enhance its security:
Best Practices
- Use strong passwords or passphrase-protected private keys.
- Disable password authentication and rely solely on public key authentication.
- Change the default SSH port (22) to a non-standard port to reduce automated attacks.
- Implement rate limiting or IP whitelisting to restrict access to trusted sources.
- Regularly update your SSH server and client software to patch known vulnerabilities.
A report by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) emphasizes the importance of securing IoT devices, as they often serve as entry points for cyberattacks.
Troubleshooting Common SSH Issues
Despite its robustness, SSH can sometimes encounter issues that prevent successful connections. Below are some common problems and their solutions:
Common Issues and Solutions
- Connection Refused: Ensure that the SSH service is running and the firewall allows traffic on the specified port.
- Authentication Failed: Verify that the username and password (or private key) are correct and match the ones configured on the IoT device.
- Timeout Errors: Check the network connectivity between your computer and the IoT device, ensuring there are no routing or DNS issues.
If you're unable to resolve the issue, consult the device's documentation or seek assistance from the manufacturer's support team.
Advanced Features and Configurations
Beyond basic connectivity, SSH offers several advanced features that can enhance your IoT device management experience:
Advanced Features
- Port Forwarding: Allows you to securely access services running on the IoT device from your local machine.
- Tunneling: Creates an encrypted tunnel for transmitting sensitive data between devices.
- Script Automation: Enables the execution of automated scripts for repetitive tasks, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
For example, you can use SSH tunneling to securely access a database running on your IoT device without exposing it directly to the internet.
Real-World Use Cases of IoT SSH Access
SSH access to IoT devices has numerous practical applications across various industries:
Use Cases
- Remote Monitoring: Use SSH to monitor the status of industrial equipment and receive real-time alerts.
- Configuration Management: Remotely configure and update IoT devices without the need for physical access.
- Security Audits: Perform security audits on IoT devices to identify vulnerabilities and implement mitigation strategies.
A case study by IBM highlights how a manufacturing company used SSH to streamline its IoT device management processes, resulting in significant cost savings and improved efficiency.
Future Trends in IoT and SSH
As technology continues to evolve, the role of SSH in IoT is expected to grow. Emerging trends such as quantum computing, edge computing, and AI-driven security will further enhance the capabilities of SSH, making it an even more powerful tool for managing IoT devices.
Research by Gartner predicts that by 2023, over 50% of enterprises will adopt edge computing strategies, increasing the demand for secure remote access solutions like SSH.
Conclusion
Accessing IoT devices via SSH is a critical skill for anyone involved in the IoT ecosystem. By following the steps outlined in this tutorial, you can securely connect to and manage your IoT devices from anywhere in the world. Remember to adhere to best practices and stay updated with the latest trends to ensure the highest level of security and efficiency.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into IoT and related technologies. Together, let's build a smarter, more connected future!